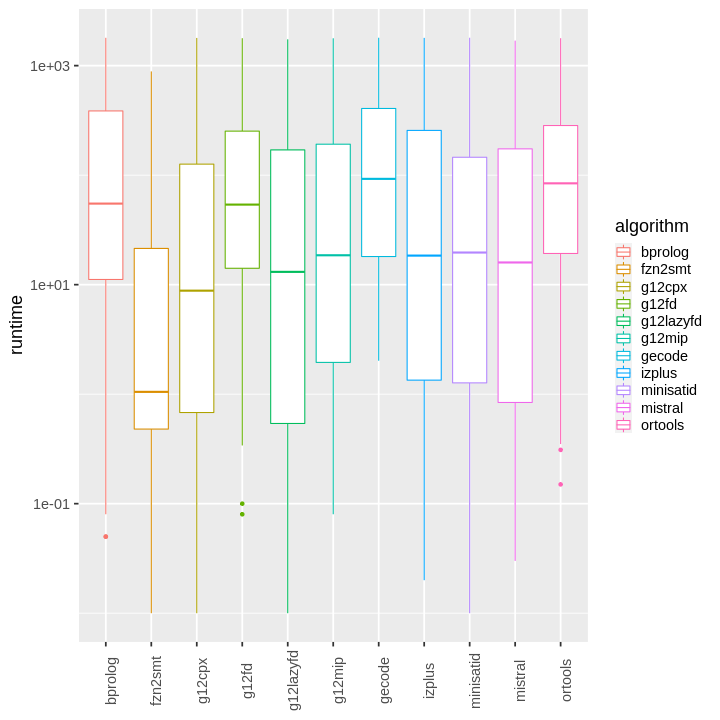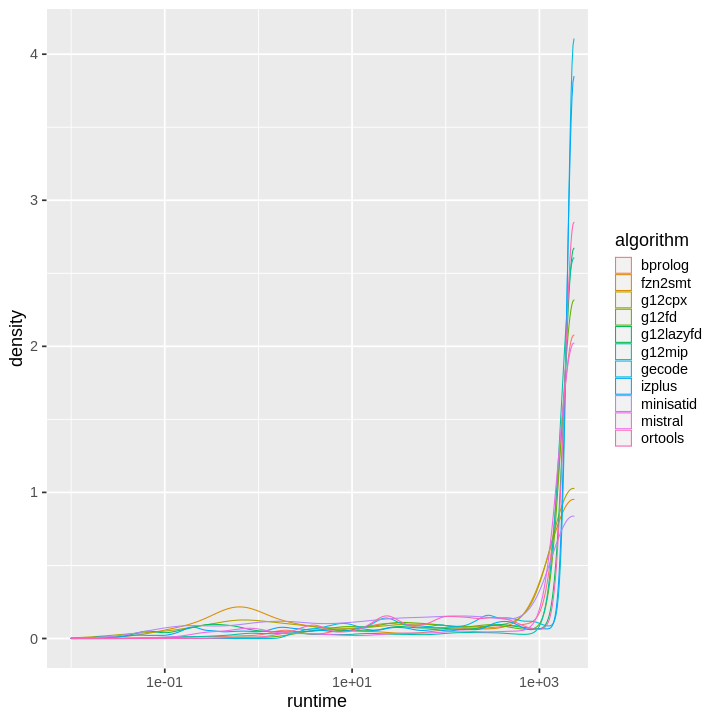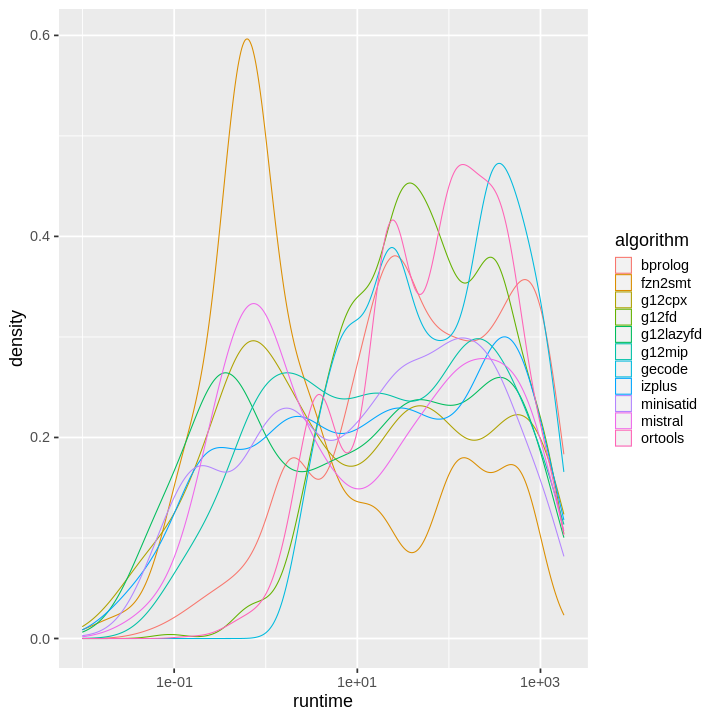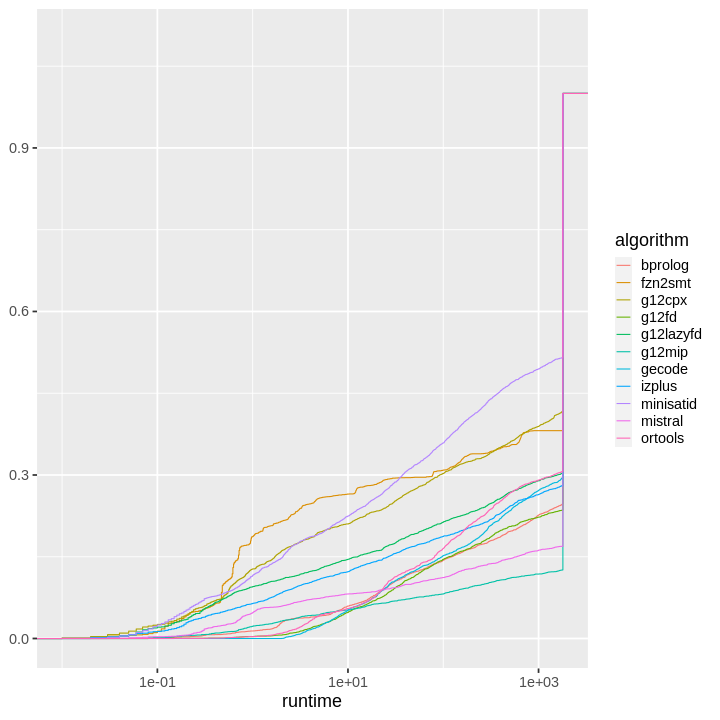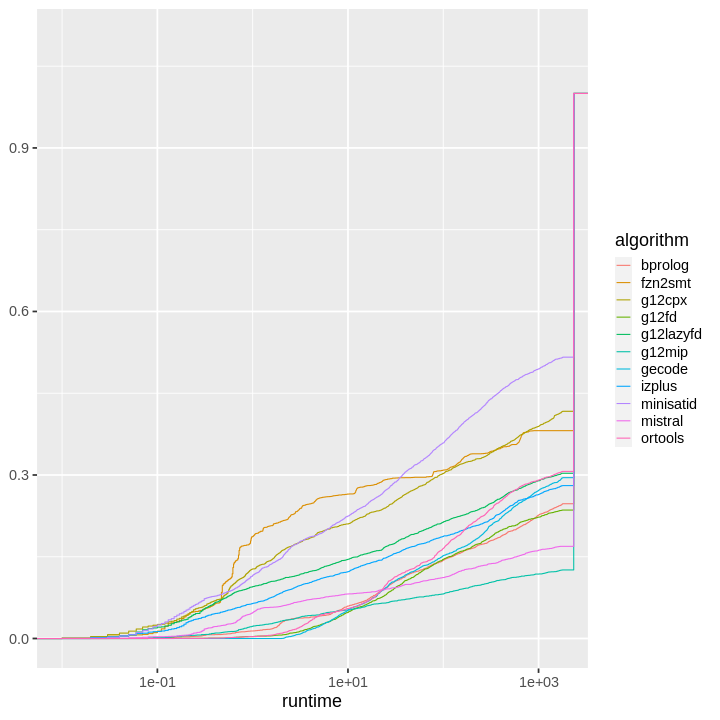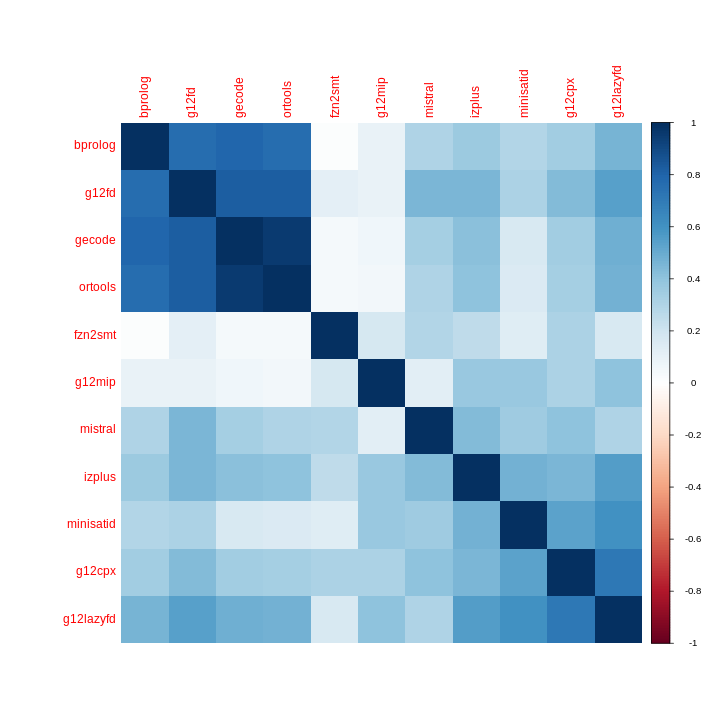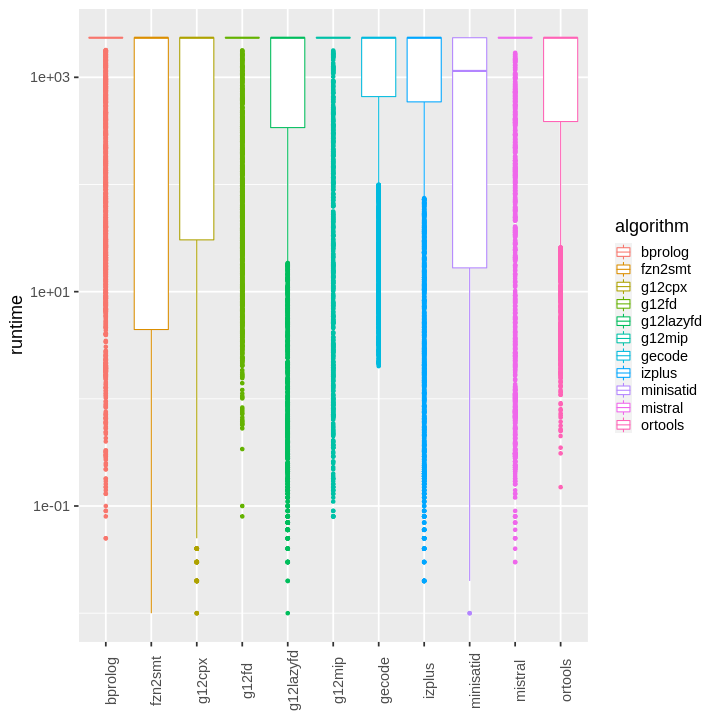
| obs | nas | min | qu_1st | med | mean | qu_3rd | max | sd | coeff_var | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bprolog | 4642 | 0 | 0.05 | 1800 | 1800 | 1423.45 | 1800 | 1800 | 689.945 | 0.484699 |
| fzn2smt | 4642 | 0 | 0.01 | 4.43 | 1800 | 1143.47 | 1800 | 1800 | 843.752 | 0.737887 |
| g12cpx | 4642 | 0 | 0.01 | 30.4275 | 1800 | 1126.98 | 1800 | 1800 | 832.378 | 0.738591 |
| g12fd | 4642 | 0 | 0.08 | 1800 | 1800 | 1424.8 | 1800 | 1800 | 695.472 | 0.488118 |
| g12lazyfd | 4642 | 0 | 0.01 | 339.392 | 1800 | 1306.1 | 1800 | 1800 | 770.814 | 0.590166 |
| g12mip | 4642 | 0 | 0.08 | 1800 | 1800 | 1597.54 | 1800 | 1800 | 548.897 | 0.34359 |
| gecode | 4642 | 0 | 2.02 | 660.837 | 1800 | 1354.65 | 1800 | 1800 | 723.121 | 0.533806 |
| izplus | 4642 | 0 | 0.02 | 590.15 | 1800 | 1350.42 | 1800 | 1800 | 744.319 | 0.551174 |
| minisatid | 4642 | 0 | 0.01 | 16.6625 | 1146.16 | 950.908 | 1800 | 1800 | 851.33 | 0.895281 |
| mistral | 4642 | 0 | 0.03 | 1800 | 1800 | 1525.83 | 1800 | 1800 | 622.611 | 0.408046 |
| ortools | 4642 | 0 | 0.15 | 386.455 | 1800 | 1316.25 | 1800 | 1800 | 751.374 | 0.570845 |
| ok | timeout | memout | not_applicable | crash | other | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bprolog | 24.731 | 61.719 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 13.550 |
| fzn2smt | 38.130 | 12.042 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 49.828 |
| g12cpx | 41.685 | 41.792 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 16.523 |
| g12fd | 23.567 | 64.821 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 11.611 |
| g12lazyfd | 30.310 | 36.514 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 33.175 |
| g12mip | 12.581 | 43.257 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 44.162 |
| gecode | 29.513 | 62.861 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 7.626 |
| izplus | 28.048 | 53.705 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 18.246 |
| minisatid | 51.616 | 32.572 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 15.812 |
| mistral | 16.911 | 66.028 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 17.062 |
| ortools | 30.655 | 62.021 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 7.324 |

## Warning: Removed 35848 rows containing non-finite values (stat_boxplot).